If you're looking to increase the traffic to your blog over the next year, SEO is a great way to do it.
Of all searches on Google, there is a split of roughly 40% of clicks going to organic results, 4% goes to paid, and 56% of searches result in no clicks at all.
That means SEO is still the most prominent channel to focus on to improve your traffic.
When you're creating content with SEO in mind, the first concept you need to realise is you're not writing for the search engine. You're writing for the users that are searching on them.
When we talk about writing for SEO, we're saying that we need to ensure our content answers search queries in a cohesive, concise, and easily understandable way.
Write for users, not search engines
While the primary focus of many SEO concepts is ensuring search engines understand your site, copywriting and article optimisation aren't one of them. Your primary focus should instead be delivering value for your audience.
Find out what your audience wants to know
The first thing you’re going to want to do once you’ve got an idea for your article is some audience research into the queries people are using to find the information you’re writing about.
I usually separate this into two sets of keywords for each topic I'm covering, one being the primary keyword and the other being secondary keywords.
What is a primary keyword?
A primary keyword should represent the overarching topic of your article. This is usually the highest volume keyword your audience searches within a topic from your research. In some cases, this is also called a parent keyword.
What are secondary keywords?
Secondary keywords represent the sub-topics you will be discussing within your article.
How do I find these keywords?
Whilst the ins and outs of doing keyword research is a bit outside the scope of this post, here are some of the best tools on the market for doing keyword research:
- Ahrefs Keyword Explorer
- SEMrush
If you haven't performed keyword research before, check this excellent blog post on Ahrefs.
Focus on informational queries
When you're completing your keyword research, you should be looking for queries that have informational intent. For example, you're never going to rank for a commercial query such a 'dell laptops'. That SERP is reserved for pages selling dell laptops.
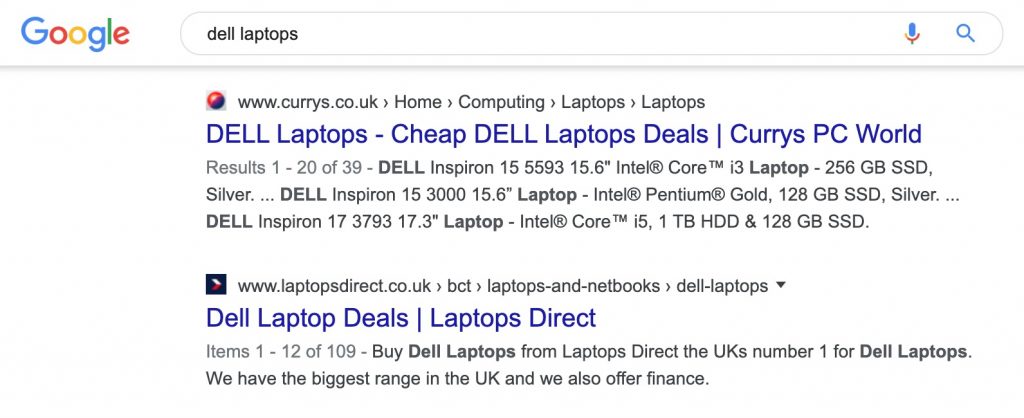
You could, however, write an article about 'best dell laptops', because the intent behind the search, in this case, is someone who is researching, not buying.
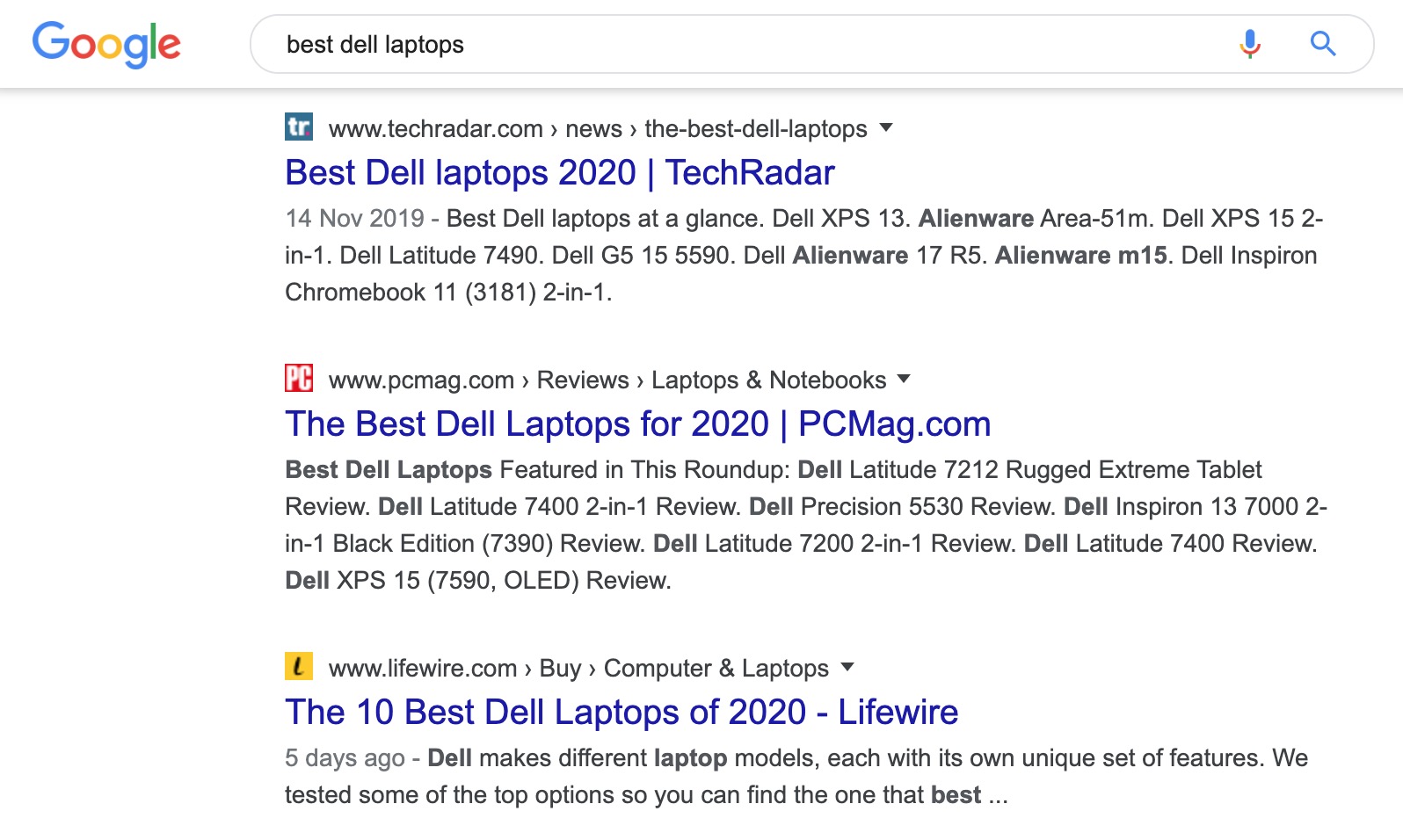
It's essential to distinguish this when researching your topic and collecting keywords. If you get this bit wrong, you'll end up writing an article on a topic you'll never rank for.
Don’t target too much
Once you have your keyword research, you want to ensure that the primary keyword or topic you’ve decided to cover isn’t too broad. I've seen a lot of cases where people complete their research on what to include in their article but end up covering things that need a separate article.
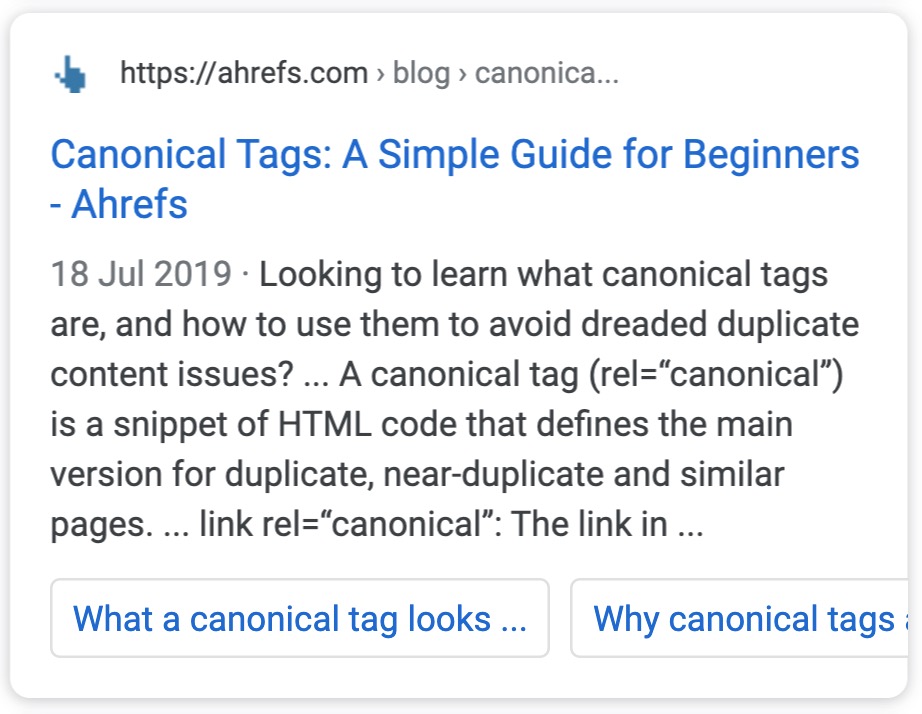
For example, if I was going to write about ‘technical SEO’ and that was my primary keyword. I may think that a secondary keyword for us to write about should be ‘canonical tags’.
That would be wrong as ‘canonical tags’ should be an entirely separate article.
The easiest way to spot this is by searching for the query and checking what appears on the search result. For example, when you search for ‘canonical tags’, you will find the below:
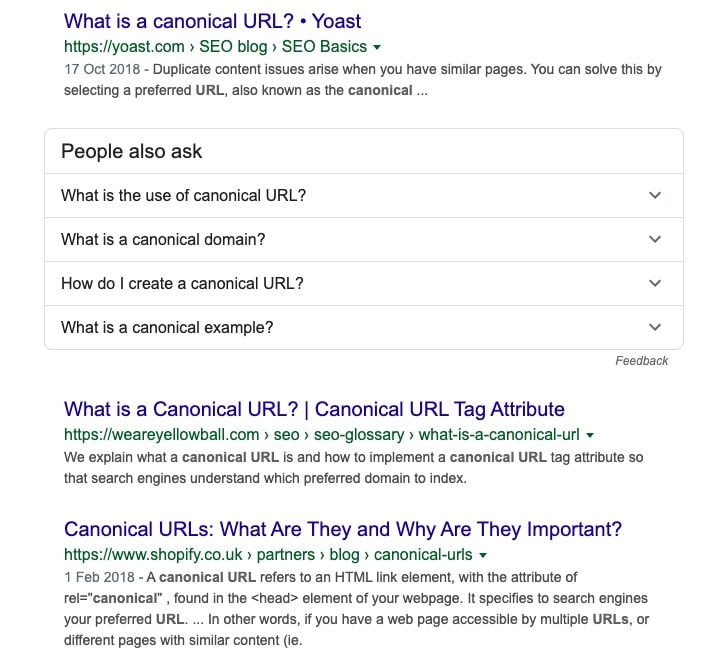
None of the results Google returns are generic articles about Technical SEO. This tells us that if I wanted to rank for that ‘what is a canonical url’ I would need to create a specific article.
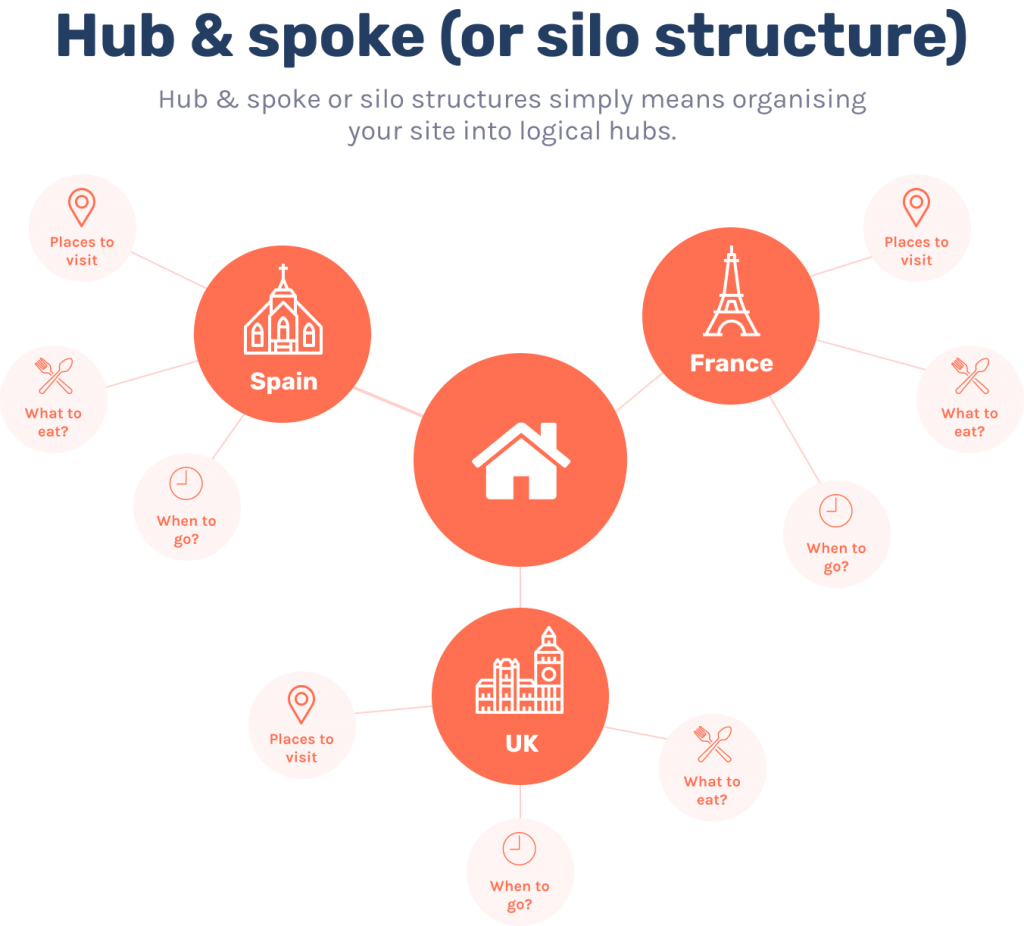
As 'what is a canonical url' is still a sub-topic of Technical SEO, what you'd want to do here is to create your Technical SEO article and then link off to any secondary pages from that main page. This is called a silo structure, hub and spoke or sometimes topic clusters. You can read more about them in my site structure article.
Make it engaging
When creating your content, you want to add value to users more than what competing articles have.
I always live by the mantra that if you aren't going to make your article better than what others have created, it isn't worth creating it.
A sure-fire way of making your content stand out is by adding various elements that make it more valuable than a standard article. That includes things like:
- An interview with an industry specialist
- Custom graphics e.g. check the graphics in my recent site structure post
- Quotes
- Video
- Interactive elements e.g. if you're providing a list of tips, consider making them filterable as I did recently with my site speed tips post
When you do things like this, you'll find that your site will begin acquiring links naturally, resulting in organic traffic increasing and acquiring more return visitors.
Optimise your alt text
What is alt text?
Alt text also called 'alt tags', is written text that describes an image that is utilised on screen readers to describe imagery to visually impaired users. Google also uses it within image search to surface images that match a user query.
Whilst Google may also use image recognition to figure out what the image is, alt text is still something you should be adding to your images for both accessibility and SEO reasons.
Google uses alt text along with computer vision algorithms and the contents of the page to understand the subject matter of the image. Also, alt text in images is useful as anchor text if you decide to use an image as a link.
Google
How to add alt text to your images
Adding alt text to your images is pretty simple. Most CMS' will have an option allowing you to add alt text when you add an image to some content. If not, it's as simple as adding the 'alt' attribute to an img element like below.
<img src="/horse.jpg" alt="a horse in a field">Code language: HTML, XML (xml)Write an awesome title tag
Creating a great title for your article that optimises for search is one of the critical things you need to get right. Your chances of ranking well are severely reduced if you write a title that doesn't relate well to your target keywords.
Here are some considerations for when you craft your title tag:
- It should contain your primary and any secondary keywords
- You need to entice users, so consider including things such as:
- Compelling stats
- A positive or negative sentiment
- Clickbait
- Include variation words e.g. '2020', 'trends' or 'best' to target long-tail search
- Keep the character count roughly around 70
If we go back to my 'canonical tags' example from earlier. Here is how we could optimise that for search:
<title>Canonical Tags - Canonicals Explained By Industry Experts | Sam Underwood</title>Code language: HTML, XML (xml)Bear in mind; you don't need to include every keyword variation. Try to have as many variations as possible whilst also making your article sound interesting.
Title tag optimisation is one of those areas of SEO that doesn't get enough ongoing focus. I'd recommend not just setting your title once and forgetting about it; try to continuously come back to it and tweak it to see the on clicks and click-through rate.
Write a meta description to entice
Whilst meta descriptions aren't going to impact how well your rank in search, they can significantly impact the likelihood of someone clicking on you within a search result. This is another area that you should focus on to improve how well your article will perform.
First, what is a meta description?
A meta description tag is an HTML tag that should summarise the content on a web page within 50 - 160 characters. Google and other search engines display this summary in their search results under the page's title.
Whilst search engines may rewrite or not use your meta description, they generally will do if it matches a users search query well.
Google will sometimes use the <meta> description tag from a page to generate a search results snippet, if we think it gives users a more accurate description than would be possible purely from the on-page content.
Google
You'll also find without the presence of social markup to say otherwise, social networks will include your meta description in the snippet whenever your URL is shared.
How do you write one?
Most CMS' allow you to edit them within the platform. If you need to write it manually, a meta description looks like the below and should be put within the <head> of your web page:
<meta name="description" content="Search the world’s information, including web pages, images, videos and more. Google has many special features to help you find exactly what you’re looking for.">Code language: HTML, XML (xml)Tips for writing a meta description
In general, when writing meta descriptions, you need to do a few things:
- Stick to the rough character count limit to prevent it from being truncated within search results
- Write compelling copy that entices users to click
- Include primary and secondary keywords as these will be bold within search results
Use structured but short and concise URLs
Setting your URL structure should be pre-planned to save lots of heartaches later on when you realise your mistakes and have to redirect lots of URLs. In general, you want some structure to your URL for a blog or article, but this may change depending on the site.
For example, if your site is just a blog similar to this one, you'll probably be fine structuring your URLs like below:
https://www.example.co.uk/blog/article-url/
If you are running a news or magazine site, you may want your article to add a bit more structure like this:
https://www.example.co.uk/lifestyle/food/article-url/
How your URL is structured depends on the site. But in general, here are some guidelines for URLs:
- Keep them short and concise
- Make sure they are easily readable
- They must contain your primary keyword
- They should be structured but not so structured the URLs become very long
- They should not repeat words
- They should be lowercase and use dashes, not underscores
I've summarised this advice in the below graphic with an example structure for a travel site that sells holidays but also contains informational content:

For articles, to keep my URLs as short as possible, I always keep the URL just containing the primary topic I'm writing about.
Take my article on site speed tips, for example.
Whilst my title is '27 tips to improve your site speed', I've kept the URL as just /resources/site-speed-tips/. This is targeting a keyword and perfectly explains what is on the page in an easily readable way.
Keeping it short has the added benefit of it not ever needing to change. For example, if I'd gone for /blog/27-site-speed-tips/ I'd of had to update my URL whenever I decided to add more tips to the URL, which is just going to get messy with redirects.
A site's URL structure should be as simple as possible. Consider organizing your content so that URLs are constructed logically and in a manner that is most intelligible to humans...
Google - Keep a simple URL structure
Structure content with headings
Structuring your articles with a correct heading structure is one of those things I see a lot of sites get wrong. You can read about HTML headers here, but the basic idea is that they are a range of tags from <h1> to <h6> that structures your content into topics and sub-topics.
For example, the H1 is the main topic of the page; this is the title of your content. The H2 is a sub-topic of the H1, an H3 under that would be the sub-topic of the H2 and so forth.
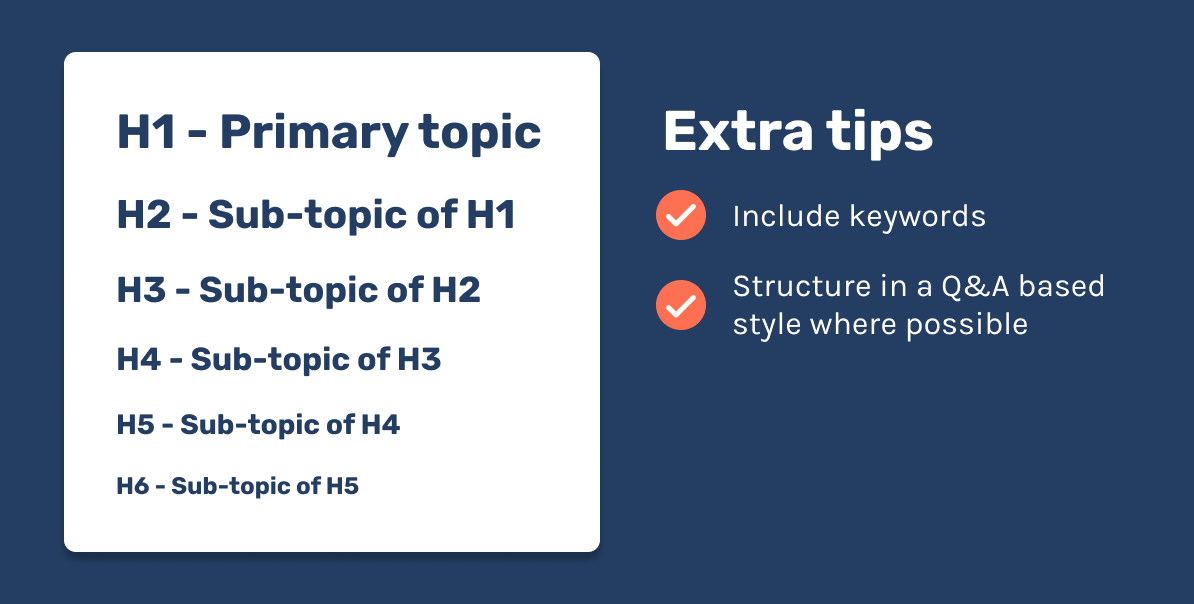
Implementing a correct heading structure can give off a strong signal to Google how your article is organised and all the topics you're covering.
Utilising headings can also impact the likelihood of you obtaining a featured snippet.
Optimise for Featured Snippets
Featured snippets have been around for a while now, and for some sites, they can be a great way to gain some additional SERP real estate and further increase your organic traffic. Ahrefs describe a Featured Snippet as:
A Featured Snippet (otherwise called Answer Box) is a brief answer to a user’s search query, which is displayed on top of Google search results. It is extracted from one of the top-ranking pages for that search query and includes that page’s title and URL.
Ahrefs
You would have seen them before. They look like this:
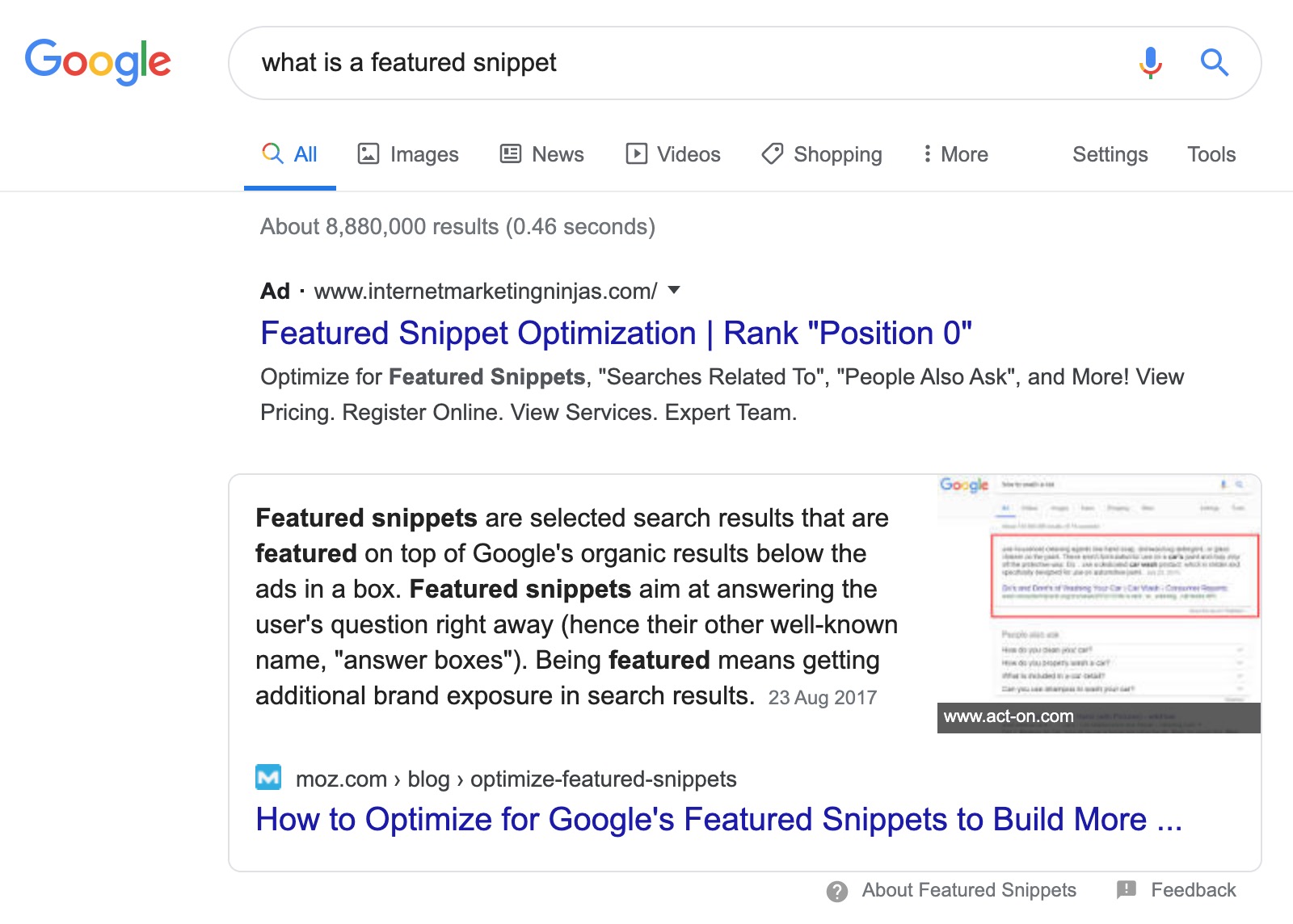
How do I show in them?
As far as capturing them, one of the main things you need to do is first to rank well. In most cases, you're going to need to rank within the top 5 to have a chance of capturing one.
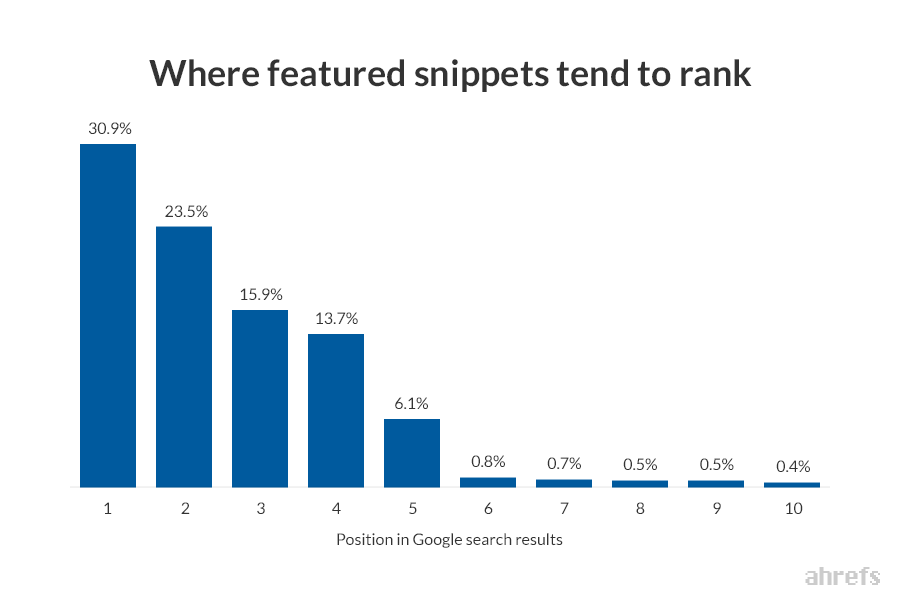
However, outside of ranking well organically, you can do a few other things to optimise for snippets.
Present information in the way Google wants
For example, if Google currently shows a list in the snippet on the search result, provide a list with similar information on your page.
Answer the query within a 50-word paragraph
If the query is informational (such as ‘what is a canonical’), try to answer the question concisely. Most snippets tend to be around 50- 55 words maximum. This advice excludes tabular data and lists.
Keep a clear subject and predicate
For example, if you were answering the question ‘what is a canonical’. Answer the question in the following manner: ‘A canonical tag is…’
Consider your HTML structure
Make sure to use lists, heading tags and tables to make it easier for Google to understand that you’re answering a question. For example, use an h2 or h3 with the text ‘What is a canonical?’ and then provide your answer succinctly under it.
I'll be writing more on this topic in the future with some examples!
Add fraggles / jump-to links
To make your article more easily navigatable, you could add something called 'fraggles' or 'jump-to' links. Google initially announced this feature back in 2009 here.
The basis of the feature is that if you provide a list of anchor links on your site Google will implement a SERP feature that allows users to navigate to the different sections of your article quickly.
You can see an example of this below:
This is great for users as it allows them to quickly find the information they are looking for within an article straight from the SERP. Built Visible has a great article on the topic of implementing them here.
Add FAQ or how-to structured data
Another thing you can do that is a bit more technical is adding structured data to your blog posts to get an enhanced snippet in search.
But first, what is Structured Data?
The Google developer guides have a great explanation of structured data below:
Structured data is a standardized format for providing information about a page and classifying the page content; for example, on a recipe page, what are the ingredients, the cooking time and temperature, the calories, and so on.
Google Developer Guides
To summarise, a standard web page is very unstructured. If a search engine wants to understand something like the cooking time of a website, it has to go through your HTML and make a good guess at what bit of text highlights the cooking time or the recipe.
With structured data, that information is clearly stated in a pre-defined format using Schema code. No guesswork involved, you declare your cooking time in some hidden code on your page, and Google collects that information and can be 100% confident the information is correct.
Because of this, Google can then include that information on the SERP as a rich result (previously called rich snippet) like below:
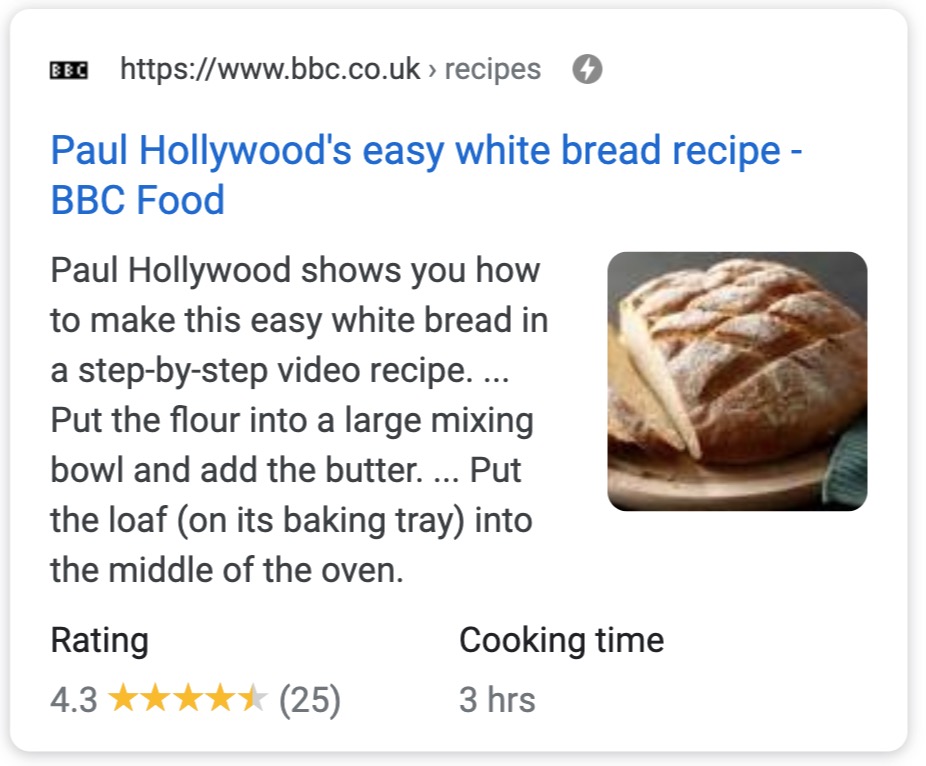
You can implement structured data in multiple formats, but the best by far is JSON-LD.
How does this relate to the blog post I'm writing?
Google recently announced a new schema type called FAQ and how-to schema. You can read the specification on adding FAQ schema here, how-to schema here and the original announcement post by Google here.
When you add these, you can get a fancy result in search like the below:
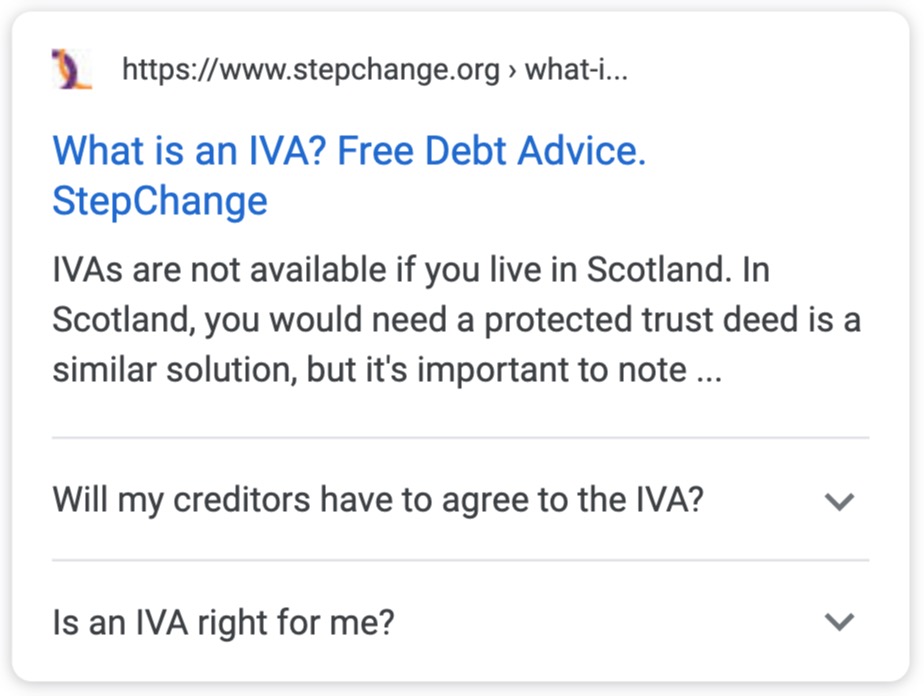

This benefits you due to an increase in SERP real estate as you get a larger listing.
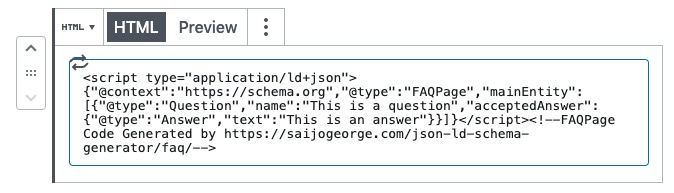
Thankfully adding this isn't too complicated. You can use the schema tool generated here and insert it into your article.
If you're on WordPress, you can add the code within an HTML block in the editor like below:
Wrapping up
Hopefully, following these tips, you'll now have some fresh ideas on how to optimise your blog posts for search in 2020.
Any questions? Feel free to comment below or tweet me @SamUnderwoodUK.